DPWX/Evolution of boundary layer echoes: 27 March 2015: Difference between revisions
Pat kennedy (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
(Fixed typos) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Author: Patrick C. Kennedy | |||
[[Image:27mar2015 2010Z Z RHI bragg anot.png|300px|right]] | |||
Boundary layer echoes observed in a CSU-CHILL RHI scan during fair weather on 27 March 2015. Time lapse loops have been prepared showing the evolution of both the elevated Bragg scattering layer and the surface-based insect echo. | |||
==Overview== | |||
Mostly clear skies existed at the CSU-CHILL radar site during the afternoon hours of 27 March 2015. Sounding data from the NWS Denver site showed that the base of a dry, stable layer existed around 4 km AGL. Solar warming of the ground surface promoted convectively driven vertical circulations within the boundary layer. Although some shallow cumulus clouds developed, there was no radar or visible evidence of precipitation. During a portion of the afternoon hours, the CSU-CHILL radar conducted a continuous series of low evelvation angle surveillance scans followed by a continuous series of RHI scans. The image sequences generated from these scans reveal several aspects of S-band (3 GHz) boundary layer echo development observed from "clear air" scatterers. | |||
==Reflectivity loop== | ==Reflectivity loop== | ||
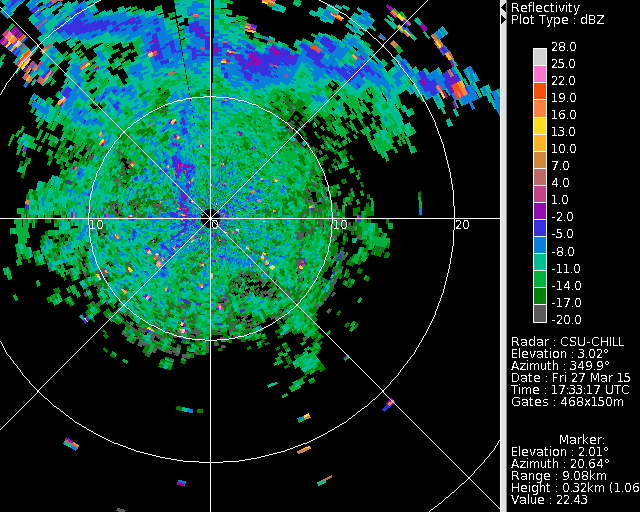
The following reflectivity images were extracted from the 3.0 deg elevation full PPI scans that were done at ~4 minute intervals. An approximately east-west oriented band of enhanced (but still low) reflectivitiy moves southward over the radar during the time period of the loop (1733 - 1931 UTC). Outside of this echo line, the mottled reflectivity patterns imply the existence various small scale vertical circulations. | |||
<center> | <center> | ||
<imgloop delay=200 imgprefix="http://www.chill.colostate.edu/anim/PCK_27mar2015_bragg_RHI/" width=640 height=512> | <imgloop delay=200 imgprefix="http://www.chill.colostate.edu/anim/PCK_27mar2015_bragg_RHI/" width=640 height=512> | ||
dBZ.CHL20150327_172915 pk360 PPI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | dBZ.CHL20150327_172915 pk360 PPI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | ||
dBZ.CHL20150327_173319 pk360 PPI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | dBZ.CHL20150327_173319 pk360 PPI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | ||
dBZ.CHL20150327_173723 pk360 PPI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | dBZ.CHL20150327_173723 pk360 PPI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | ||
| Line 37: | Line 49: | ||
==Radial velocity loop== | ==Radial velocity loop== | ||
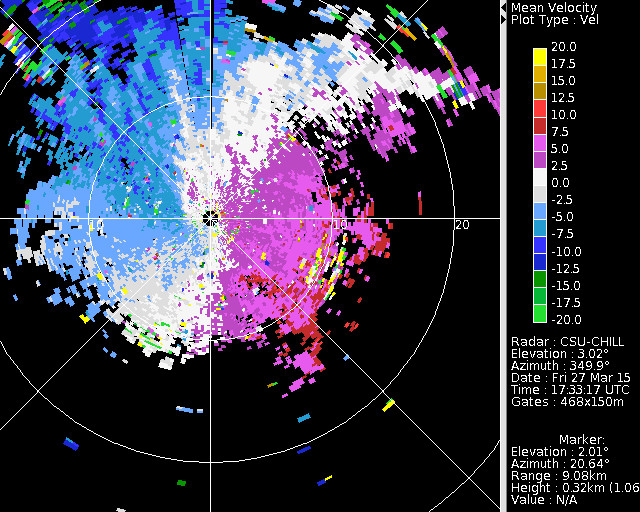
The following loop shows the radial velocity patterns from the same PPI scans that were used in the preceding reflectivity loop. The passage of the echo line was associated with a shift in the low-level wind direction from westerly to northwesterly; the wind speeds also increased appreciably. (This can be seen by alternating between the first and last loop frames.) | |||
<center> | <center> | ||
<imgloop delay=200 imgprefix="http://www.chill.colostate.edu/anim/PCK_27mar2015_bragg_RHI/" width=640 height=512> | <imgloop delay=200 imgprefix="http://www.chill.colostate.edu/anim/PCK_27mar2015_bragg_RHI/" width=640 height=512> | ||
Vel.CHL20150327_172915 pk360 PPI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | Vel.CHL20150327_172915 pk360 PPI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | ||
Vel.CHL20150327_173319 pk360 PPI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | Vel.CHL20150327_173319 pk360 PPI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | ||
Vel.CHL20150327_173723 pk360 PPI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | Vel.CHL20150327_173723 pk360 PPI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | ||
| Line 74: | Line 87: | ||
==RHI reflectivity loop== | ==RHI reflectivity loop== | ||
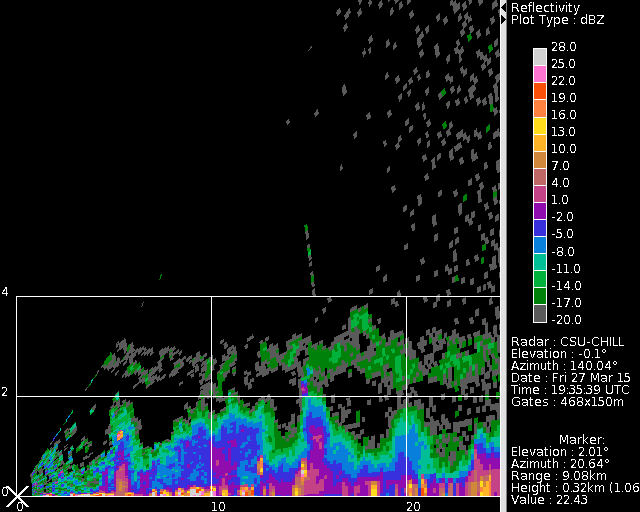
Following the PPI scan interval shown above, the radar shifted into continuous RHI scan mode. These two-sweep RHI volume were oriented along the echo line located southeast of the radar. (Up sweep azimuth of 136 degrees and down sweep azimuth of 140 degrees.) The following image loop was assembled from the 140 degree azimuth reflectivity images. Reflectivities were the strongest at near-surface heights. Based on the highly positive <math>Z_{dr}</math> values in the surface layer (data to be shown later), insects were probably responsible for the low altitude echo. A separate, perturbed layer of very low reflectivity was consistently present in the 3 - 4 km AGL height levels. This elevated echo was probably due to Bragg scattering generated by turbulence-driven moisture and temperature perturbations along the base of the stable layer that capped the boundary layer. The smaller-scale "mantle echoes" occurred in the sharp thermodynamic gradients along the sides and tops of cumulus clouds [Knight and Miller 1993]. The amplitude of these cumulus cloud echoes and the average height of the Bragg scattering layer is also seen to increase with time. (Note: The unequal range and height axis scaling in these plots causes the echo patterns to be stretched in the vertical in the loop image frames). | |||
<center> | <center> | ||
<imgloop delay=300 imgprefix="http://www.chill.colostate.edu/anim/PCK_27mar2015_bragg_RHI/" width=640 height=512> | <imgloop delay=300 imgprefix="http://www.chill.colostate.edu/anim/PCK_27mar2015_bragg_RHI/" width=640 height=512> | ||
dBZ.CHL20150327_193335 rhi2 RHI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | dBZ.CHL20150327_193335 rhi2 RHI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | ||
dBZ.CHL20150327_193543 rhi2 RHI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | dBZ.CHL20150327_193543 rhi2 RHI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | ||
dBZ.CHL20150327_193750 rhi2 RHI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | dBZ.CHL20150327_193750 rhi2 RHI Sweep 02 Plot 0.png | ||
| Line 107: | Line 121: | ||
</imgloop> | </imgloop> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
==Data from selected times== | |||
The following photograph of the sky was taken looking southeast from the radar site at 1948 UTC. The RHI azimuths are located near the center of the image. The clouds are fair weather cumulus. The vertical development of these clouds typically stops when they are unable to penetrate elevated "capping layers" of high thermal stability. | |||
[[Image:27mar2015 CU cropped.JPG|center]] | [[Image:27mar2015 CU cropped.JPG|center]] | ||
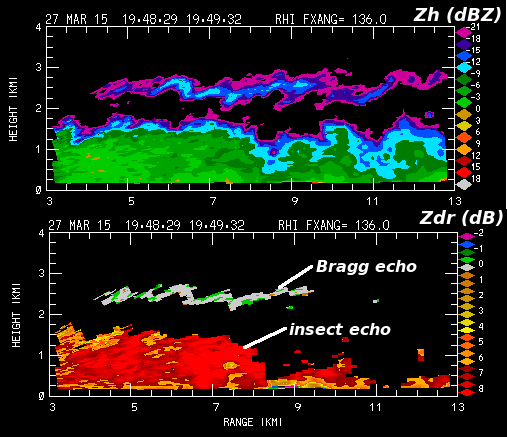
The next RHI shows the reflectivity and differential reflectivity (<math>Z_{dr}</math>) data observed at very nearly the same time as the preceding photograph. As noted earlier, the boundary layer <math>Z_{dr}</math> values are on the order of +7 dB, indicative of the highly oblate cross sections of insects. In contrast, the chaotic turbulent motions associated with the Bragg echoes tend to return nearly equal horizontally and vertically-polarized returned signal levels, yielding ~0 dB <math>Z_{dr}</math> values. Similar results have been reported by Wilson et al [Wilson et al 1994: Fig. 9] | |||
[[Image:27mar2015 1948 Z Zdr RHI anot.png|center]] | [[Image:27mar2015 1948 Z Zdr RHI anot.png|center]] | ||
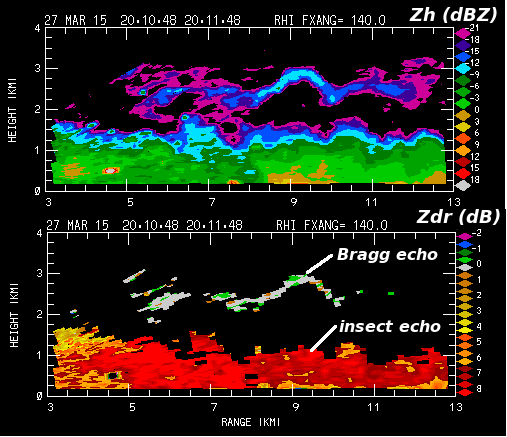
The final plot is a similar <math>Z_h</math>, <math>Z_{dr}</math> plot taken from a later time (2010 UTC) when a cumulus cloud mantle echo was more evident. The contrasting <math>Z_{dr}</math> regimes between the insect and Bragg layers was maintained throughout the observational period. | |||
[[Image:27mar2015 2009 Z Zdr RHI anot.png|center]] | [[Image:27mar2015 2009 Z Zdr RHI anot.png|center]] | ||
==References== | |||
* [*Knight and Miller 1993] Charles A. Knight and L. J. Miller, 1993: [http://dx.doi.org/10.1175%2F1520-0477(1993)074%3C0179%3AFREFCC%3E2.0.CO%3B2 First Radar Echoes from Cumulus Clouds.] Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 74, 179–188. | |||
* [*Wilson et al 1994] James W. Wilson, Tammy M. Weckwerth, J. Vivekanandan, Roger M. Wakimoto, and Robert W. Russell, 1994: [http://dx.doi.org/10.1175%2F1520-0426(1994)011%3C1184%3ABLCARE%3E2.0.CO%3B2 Boundary Layer Clear-Air Radar Echoes: Origin of Echoes and Accuracy of Derived Winds.] J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 11, 1184–1206. | |||
[[Category:Featured Articles]] | |||
[[Category:Boundary Layer]] | |||
Latest revision as of 13:10, 11 May 2015
Author: Patrick C. Kennedy
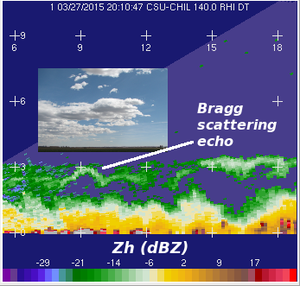
Boundary layer echoes observed in a CSU-CHILL RHI scan during fair weather on 27 March 2015. Time lapse loops have been prepared showing the evolution of both the elevated Bragg scattering layer and the surface-based insect echo.
Overview
Mostly clear skies existed at the CSU-CHILL radar site during the afternoon hours of 27 March 2015. Sounding data from the NWS Denver site showed that the base of a dry, stable layer existed around 4 km AGL. Solar warming of the ground surface promoted convectively driven vertical circulations within the boundary layer. Although some shallow cumulus clouds developed, there was no radar or visible evidence of precipitation. During a portion of the afternoon hours, the CSU-CHILL radar conducted a continuous series of low evelvation angle surveillance scans followed by a continuous series of RHI scans. The image sequences generated from these scans reveal several aspects of S-band (3 GHz) boundary layer echo development observed from "clear air" scatterers.
Reflectivity loop
The following reflectivity images were extracted from the 3.0 deg elevation full PPI scans that were done at ~4 minute intervals. An approximately east-west oriented band of enhanced (but still low) reflectivitiy moves southward over the radar during the time period of the loop (1733 - 1931 UTC). Outside of this echo line, the mottled reflectivity patterns imply the existence various small scale vertical circulations.
|
|
||
|
Radial velocity loop
The following loop shows the radial velocity patterns from the same PPI scans that were used in the preceding reflectivity loop. The passage of the echo line was associated with a shift in the low-level wind direction from westerly to northwesterly; the wind speeds also increased appreciably. (This can be seen by alternating between the first and last loop frames.)
|
|
||
|
RHI reflectivity loop
Following the PPI scan interval shown above, the radar shifted into continuous RHI scan mode. These two-sweep RHI volume were oriented along the echo line located southeast of the radar. (Up sweep azimuth of 136 degrees and down sweep azimuth of 140 degrees.) The following image loop was assembled from the 140 degree azimuth reflectivity images. Reflectivities were the strongest at near-surface heights. Based on the highly positive values in the surface layer (data to be shown later), insects were probably responsible for the low altitude echo. A separate, perturbed layer of very low reflectivity was consistently present in the 3 - 4 km AGL height levels. This elevated echo was probably due to Bragg scattering generated by turbulence-driven moisture and temperature perturbations along the base of the stable layer that capped the boundary layer. The smaller-scale "mantle echoes" occurred in the sharp thermodynamic gradients along the sides and tops of cumulus clouds [Knight and Miller 1993]. The amplitude of these cumulus cloud echoes and the average height of the Bragg scattering layer is also seen to increase with time. (Note: The unequal range and height axis scaling in these plots causes the echo patterns to be stretched in the vertical in the loop image frames).
|
|
||
|
Data from selected times
The following photograph of the sky was taken looking southeast from the radar site at 1948 UTC. The RHI azimuths are located near the center of the image. The clouds are fair weather cumulus. The vertical development of these clouds typically stops when they are unable to penetrate elevated "capping layers" of high thermal stability.

The next RHI shows the reflectivity and differential reflectivity () data observed at very nearly the same time as the preceding photograph. As noted earlier, the boundary layer values are on the order of +7 dB, indicative of the highly oblate cross sections of insects. In contrast, the chaotic turbulent motions associated with the Bragg echoes tend to return nearly equal horizontally and vertically-polarized returned signal levels, yielding ~0 dB values. Similar results have been reported by Wilson et al [Wilson et al 1994: Fig. 9]
The final plot is a similar , plot taken from a later time (2010 UTC) when a cumulus cloud mantle echo was more evident. The contrasting regimes between the insect and Bragg layers was maintained throughout the observational period.
References
- [*Knight and Miller 1993] Charles A. Knight and L. J. Miller, 1993: First Radar Echoes from Cumulus Clouds. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 74, 179–188.
- [*Wilson et al 1994] James W. Wilson, Tammy M. Weckwerth, J. Vivekanandan, Roger M. Wakimoto, and Robert W. Russell, 1994: Boundary Layer Clear-Air Radar Echoes: Origin of Echoes and Accuracy of Derived Winds. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 11, 1184–1206.