DPWX/Dual polarization hail signatures observed by the CSU-CHILL and NWS KCYS radars: 23 June 2014: Difference between revisions
Pat kennedy (talk | contribs) (initial image posting) |
Pat kennedy (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Overview== | |||
Hailstones, especially those with diameters above ~1.9 cm (.75 inches), undergo large, nearly random fluctuations in orientation as they fall. Their shapes are also typically quasi-spherical. These characteristics cause their backscattering cross sections to be nearly equal with respect to the horizontally and vertically polarized illumination provided by a dual polarization weather radar. In contrast, the balance of the aerodynamic and surface tension forces acting on falling raindrops tends to deform them into oblate (flattened) spheriods. Thus, raindrops (especially for diameters > 1 mm) consistently present a backscattering cross section that is larger for H waves than for V waves. This preferred orientation causes the horizontally polarized return signal received from raindrops to be stronger than the vertically polarized received signal. In contrast, the H and V signals levels returned by hailstones will be more nearly equal. These effects are seen in differential reflectivity (Zdr) field output by dual polarization radars. Zdr is the ratio of the H to V return signal levels expressed on a logarithmetric scale. Under this definition, the quasi-equal H and V received signal levels produced by hail will give Zdr values near 0 dB, while oblate raindrops will produce Zdr values in the general +0.75 to +4 dB range. These Zdr variations are among the dual polarization signatures that were observed by the CSU-CHILL and NWS KCYS radars on 23 June 2014. | |||
==CSU-CHILL RHI data== | |||
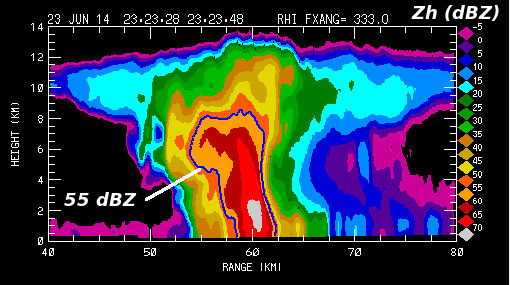
The following data plots were made from an RHI scan conducted by the CSU-CHILL radar at 2323 UTC through the reflectivity core of a hailstorm on 23 June 2014. maximum reflectivity levels exceeded 70 dBZ in a small area near the 60 km range point. The overhanging reflectivity configuration on the near range side of the storm and the domed echo summit indicate that a strong updraft was present. (For reference, the 55 dBZ reflectivity contour is included in all of the RHI plots). | |||
[[Image:01 23jun2014 chill rhi z.png|center]] | [[Image:01 23jun2014 chill rhi z.png|center]] | ||
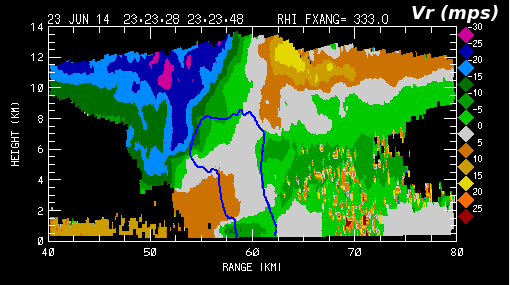
The corresponding radial velocity pattern contains surface convergence at the near range edge of the reflectivity core, and divergence centered on the echo summit is evident at the anvil level. The vertical alignment of these two features suggests that they are connected by a well defined updraft. The smooth radial velocity patterns are disrupted at heights below ~8 km AGL and ranges beyond the reflectivity core. This disruption is a consequence of the three body scattering interactions that were taking place between the highly reflective scatterers in the echo core aloft and the underlying ground surface (Wilson and Reum, JTEC 1988, p197-205). | |||
[[Image:02 23jun2014 chill rhi vt.png|center]] | [[Image:02 23jun2014 chill rhi vt.png|center]] | ||
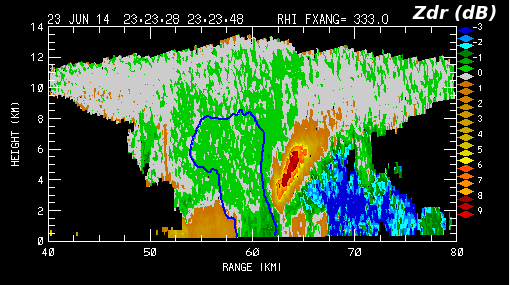
The next plot shows the corresponding Zdr field. Zdr values of 0 dB and lower are found at the surface in the echo core region where a significant concentration of hailstones exists. Slightly negative Zdr values have been previously reported in areas of moderate to large diameter hailstones (Zrnic ref). In agreement with Hubbert and Bringi (JTEC 2000, p 51-61), the three body scattering region is marked by distinctly positive Zdr values at higher elevation angles and negative values at near surface elevations. | |||
[[Image:03 23jun2014 chill rhi zdr.png|center]] | [[Image:03 23jun2014 chill rhi zdr.png|center]] | ||
==KCYS PPI data== | |||
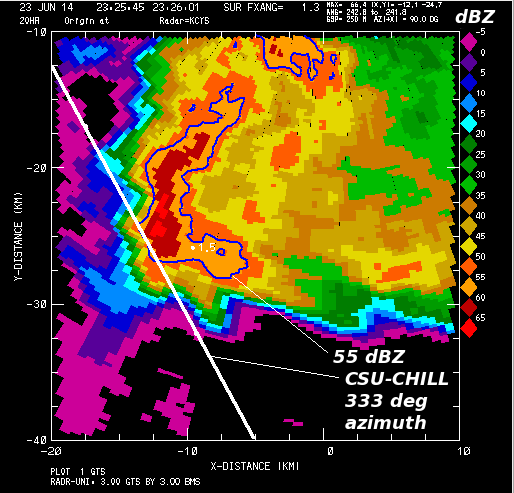
The NWS radar in Cheyenne Wyoming (KCYS) was collecting data from this same storm at relatively short range (~40 km). Data from the KCYS 1.3 degree elevation angle scan taken at ~2325 UTC is shown below. As outlined by the 55 dBZ reflectivity contour, the low level reflectivity core assumed an 'L" shaped configuration at this time. Due to three body scattering down range from KCYS, a lower reflectivity appendage extended southwestward from the echo core. | |||
[[Image:04 23jun2014 kcys z.png|center]] | [[Image:04 23jun2014 kcys z.png|center]] | ||
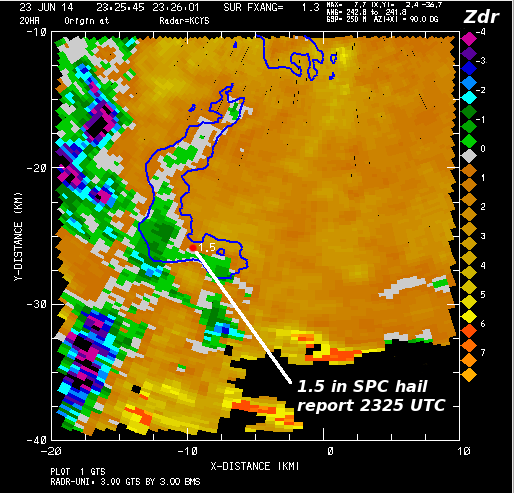
The corresponding KCYS Zdr field is shown below. The presence of hail has reduced the Zdr to near 0 dB in much of the echo core. The existence of hail was confirmed by an SPC report of 1.5 inch diameter hail that was reported at 2325 UTC. As was the case in the CHILL RHI data, negative Zdr values were prevelant in the three body scattering region at this low elevation angle. | |||
[[Image:05 23jun2014 kcys zdr.png|center]] | [[Image:05 23jun2014 kcys zdr.png|center]] | ||
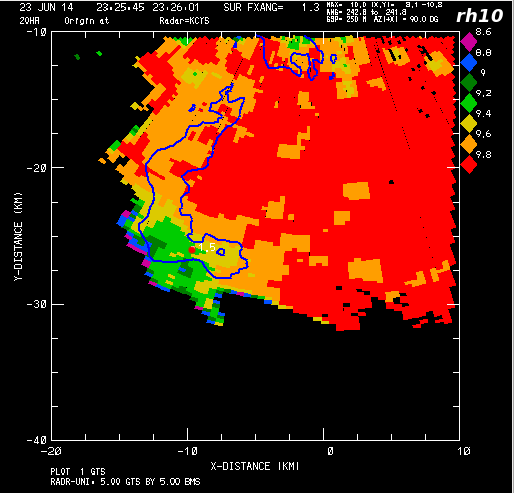
In addition to near 0 dB Zdr values, the hail can reduce the correlation between the co-polar H and V received signals (rhoHV). This reduction is increased when the hailstones have significant shape irregularities and when hailstones are mixed with rain, producing a wide variety of particle shapes and diameters within the radar pulse volume. | |||
[[Image:06 23jun2014 kcys rh10.png|center]] | [[Image:06 23jun2014 kcys rh10.png|center]] | ||
Revision as of 17:19, 31 July 2014
Overview
Hailstones, especially those with diameters above ~1.9 cm (.75 inches), undergo large, nearly random fluctuations in orientation as they fall. Their shapes are also typically quasi-spherical. These characteristics cause their backscattering cross sections to be nearly equal with respect to the horizontally and vertically polarized illumination provided by a dual polarization weather radar. In contrast, the balance of the aerodynamic and surface tension forces acting on falling raindrops tends to deform them into oblate (flattened) spheriods. Thus, raindrops (especially for diameters > 1 mm) consistently present a backscattering cross section that is larger for H waves than for V waves. This preferred orientation causes the horizontally polarized return signal received from raindrops to be stronger than the vertically polarized received signal. In contrast, the H and V signals levels returned by hailstones will be more nearly equal. These effects are seen in differential reflectivity (Zdr) field output by dual polarization radars. Zdr is the ratio of the H to V return signal levels expressed on a logarithmetric scale. Under this definition, the quasi-equal H and V received signal levels produced by hail will give Zdr values near 0 dB, while oblate raindrops will produce Zdr values in the general +0.75 to +4 dB range. These Zdr variations are among the dual polarization signatures that were observed by the CSU-CHILL and NWS KCYS radars on 23 June 2014.
CSU-CHILL RHI data
The following data plots were made from an RHI scan conducted by the CSU-CHILL radar at 2323 UTC through the reflectivity core of a hailstorm on 23 June 2014. maximum reflectivity levels exceeded 70 dBZ in a small area near the 60 km range point. The overhanging reflectivity configuration on the near range side of the storm and the domed echo summit indicate that a strong updraft was present. (For reference, the 55 dBZ reflectivity contour is included in all of the RHI plots).
The corresponding radial velocity pattern contains surface convergence at the near range edge of the reflectivity core, and divergence centered on the echo summit is evident at the anvil level. The vertical alignment of these two features suggests that they are connected by a well defined updraft. The smooth radial velocity patterns are disrupted at heights below ~8 km AGL and ranges beyond the reflectivity core. This disruption is a consequence of the three body scattering interactions that were taking place between the highly reflective scatterers in the echo core aloft and the underlying ground surface (Wilson and Reum, JTEC 1988, p197-205).
The next plot shows the corresponding Zdr field. Zdr values of 0 dB and lower are found at the surface in the echo core region where a significant concentration of hailstones exists. Slightly negative Zdr values have been previously reported in areas of moderate to large diameter hailstones (Zrnic ref). In agreement with Hubbert and Bringi (JTEC 2000, p 51-61), the three body scattering region is marked by distinctly positive Zdr values at higher elevation angles and negative values at near surface elevations.
KCYS PPI data
The NWS radar in Cheyenne Wyoming (KCYS) was collecting data from this same storm at relatively short range (~40 km). Data from the KCYS 1.3 degree elevation angle scan taken at ~2325 UTC is shown below. As outlined by the 55 dBZ reflectivity contour, the low level reflectivity core assumed an 'L" shaped configuration at this time. Due to three body scattering down range from KCYS, a lower reflectivity appendage extended southwestward from the echo core.
The corresponding KCYS Zdr field is shown below. The presence of hail has reduced the Zdr to near 0 dB in much of the echo core. The existence of hail was confirmed by an SPC report of 1.5 inch diameter hail that was reported at 2325 UTC. As was the case in the CHILL RHI data, negative Zdr values were prevelant in the three body scattering region at this low elevation angle.
In addition to near 0 dB Zdr values, the hail can reduce the correlation between the co-polar H and V received signals (rhoHV). This reduction is increased when the hailstones have significant shape irregularities and when hailstones are mixed with rain, producing a wide variety of particle shapes and diameters within the radar pulse volume.