Differential attenuation patterns: 19 August 2011
Introduction
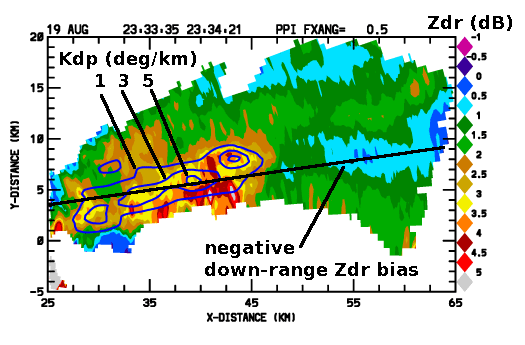
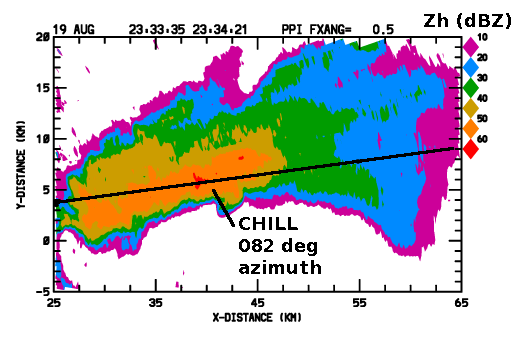
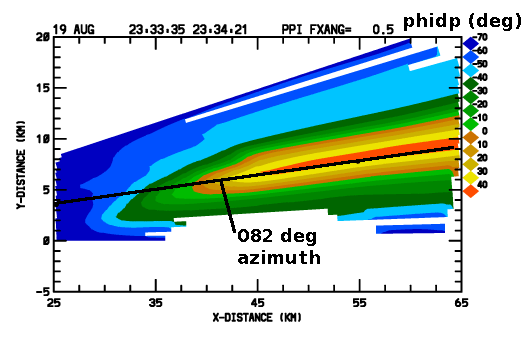
Scattered thunderstorms developed in several portions of the CSU-CHILL coverage area during the afternoon hours of 19 August 2011. For an ~10 minute time period, the storms developing a short distance east of the radar produced an echo pattern with a maximum reflectivity axis that was radially aligned with the radar. Radar pulses propagating along this heavy rain axis experienced the accumulated effects of high concentrations of oblate raindrops: The greater retardation experienced by the H polarized waves relative to the V polarized waves caused large differential propagation phase () shifts to be observed. The oblate drops also made the attenuation losses greater for the H waves than for the V waves. The resultant preferential weakening of the H signal level introduced a negative bias into the Differential Reflectivity ( ) values.These effects are shown in the following plots made from a low elevation PPI scan through the heavy rain area.
Reflectivity
Differential propagation phase ()
Differential reflectivity ()