Clock Generator User's Guide (TN-007)
This article describes the Clock Generator Module developed at the CSU-CHILL facility. It is capable of generating up to eight low-jitter clocks up to 1.6 GHz, depending on the configuration. Various logic families are supported, including LVPECL, LVDS and 3.3V CMOS. This design is primarily for the Solid-state X-band project, however, it is flexible enough to serve the needs of the CSU-CHILL and CSU-Pawnee radar systems.
Block Diagram
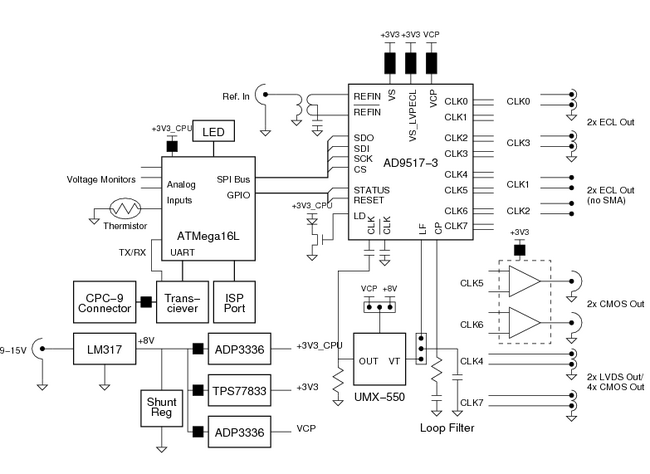
The figure shows a block diagram of the clock generator. An Atmel ATmega16L microcontroller is the primary control device. An Analog Devices AD9517 Clock Generator chip is used to implement the clock generation and distribution functions. The AD9517 is controlled by the ATmega16L through an SPI-compatible serial bus. In addition, the microcontroller monitors the AD9517's status through several general-purpose I/O lines. The AD9517 phase-locks a United Microwave UMX-550 1.92 GHz PLL to the input reference clock. The AD9517 outputs are brought out to ten SMA connectors.
The microcontroller communicates with a host machine through an RS-485 interface. The microcontroller firmware presents a Modbus/RTU interface, permitting external devices to program registers on the clock generator, and to poll its running status.
A significant portion of the design is dedicated to power supplies. This is to ensure that the clock generator chip and VCO are powered from clean, noise-free supplies to ensure the least possible jitter due to power supply ripple and noise.
The entire design is contained within an RF-tight aluminum enclosure to prevent leakage of the clock signals, and also to protect the VCO from external interference.
Clock Generator Block Diagram
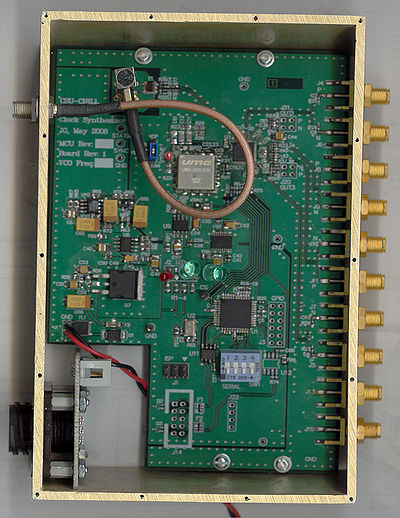
Clock Generator - Top View
Components
Microcontroller
The microcontroller used on this design is the Atmel ATmega16L, a low-power 8-bit microcontroller with 16kB of Flash, 1k SRAM and 512 bytes of EEPROM. The ATmega series of controllers is chosen since they provide an inexpensive means of controlling remote devices, and open-source programming tools such as WinAVR are available. Several on-board peripherals are available, including an eight-channel ADC, timers, USART and general-purpose I/O. The microcontroller is clocked by a 7.3728 MHz crystal oscillator. The frequency is chosen to be a multiple of popular serial port baud rates such as 9600 bps.
The SPI port on the microcontroller is used to communicate with the AD9517 clock generator. This allows the MCU to set and read the registers on the AD9517.
The USART is used to communicate with a host through the Modbus/RTU protocol. A MAX3072 transceiver is used to perform level conversion and differential to single-ended conversion of the RS-485 bus. The MAX3072 controls the rise-time of the RS-485 bus to reduce the chance of interference.
The onboard 8-channel, 10-bit ADC is used to sample the various voltages present on the board, as well as to measure the board temperature using an NTC thermistor. The MCU performs linearization of the thermistor voltage, converting it to a temperature reading.
Reference Input
The reference frequency to which the PLL within the clock generator locks to is brought in through the reference input. An SMA single-ended input is used, and a Mini-circuits BALUN is used to convert this to a balanced signal. The balanced signal is fed to the Clock Generator chip. Proper biasing of the signals is necessary for the BALUN to function correctly.
The default configuration of the clock generator board accepts a 10 MHz reference frequency, at 0 - +10 dBm. By reprogramming the reference divider within the AD9517, any reference frequency up to 250 MHz may be used.
Clock Generator
The AD9517 clock generator performs the majority of the functions on the board. It consists of a 2.4 GHz PLL, an integral 2 GHz VCO and a clock distribution network. The clock distribution section of the chip includes various dividers that may be applied to the VCO output. Up to twelve outputs are available, although in this design, only ten may be used at once (depending on the operating mode and configuration).
The reference input is driven by the balanced reference input frequency. Only one reference is available on the AD9517 in the differential mode. The AD9517 is powered using a 3.3V supply for the main supply, and a separate 5V supply for the charge pump. An external loop filter is attached to the charge pump output to set the loop bandwidth of the PLL. The AD9517 is configured by default in the external VCO mode, and the internal VCO is powered down. In order to use the internal VCO, the Charge Pump power supply must be reconfigured using resistors to operate at 3.3V, and other resistors must be reconfigured to deliver the loop filter output to the internal VCO control pin. In the external VCO configuration, any external PLL with the standard 16-pad layout and supply voltage up to 8V can be used.
The output of the VCO is connected to the input of the clock distribution section of the AD9517. The AD9517 provides four programmable dividers, which are then used to drive the various output signals.
In the default configuration, the outputs are set up as follows:
| Outputs | Frequency | Standard | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| OUT0 | 960 MHz | LVPECL | 600 mVpp swing, AC coupled |
| OUT1 | 960 MHz | LVPECL | Not available on SMA |
| OUT2 | 160 MHz | LVPECL | Not available on SMA |
| OUT3 | 160 MHz | LVPECL | 600 mVpp swing, AC coupled |
| OUT4 | 160 MHz | LVDS | DC coupled |
| OUT5 | 160 MHz | CMOS | Configured on the AD9517 as LVDS, see text |
| OUT6 | 40 MHz | CMOS | Configured on the AD9517 as LVDS, see text |
| OUT7 | 40 MHz | LVDS | DC coupled |
Clock Output Configuration
The outputs OUT5 and OUT6 have LVDS line receivers on the clock synthesizer board, which output single-ended 3.3V CMOS signals. Thus, the AD9517 must be configured to drive these outputs as LVDS.
OUT4 and OUT7 may be reconfigured on the AD9517 as CMOS outputs, in which case each SMA may be independently used. In this configuration, however, the CMOS outputs must not be heavily loaded. While capable of driving a 50 ohm load, the output swing under these conditions may not meet the 3.3V CMOS specifications. The outputs are also not designed to drive highly capacitive cable loads.
The Loop Filter is designed to meet the needs of a specific application and VCO. The Analog Devices ADsimclk software may be used to interactively design new loop filters. Space is provided on the board to design up to a third-order filter.
The serial port is connected to the MCU SPI bus, to permit register programming.
The Lock Detect output drives a MOSFET, which in turn drives a lock-detect LED. The default configuration on the AD9517 uses the LD output as an Analog Lock Detect, and the MOSFET gate capacitance behaves as the low-pass filter. The STATUS output is programmed to go low if the PLL goes out of lock, the reference is below a threshold frequency or the VCO is operating below a threshold frequency. The STATUS pin is connected to an interrupt line on the MCU, which permits the MCU to identify faults.
VCO
The clock generator board accepts any VCO that uses the standard MINI-16 half-inch VCO package offered by several manufacturers such as UMX, Sirenza and Z Communications. The VCO must have the following characteristics:
| Characteristic | Parameter | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 2.4 GHz Max | |
| Supply | 3.3 - 8V | Up to 15V may be used, with modifications to the board |
| Tuning voltage | 0 - 5.5V | Smaller ranges require jumper programming |
VCO Configuration
The best phase noise characteristics are obtained by using narrow-band VCOs, such as those based on Ceramic Resonant Oscillator technology (typical tuning range is a few MHz). The default configuration of the clock synthesizer uses the UMX-550 VCO from UMX. This VCO requires a supply voltage of 8V, with a 5V tuning voltage range and has a center frequency of 1.92 GHz.
Output Conditioning
The LVPECL outputs are terminated with a 200 ohm resistor, and are capacitor-coupled to the output SMA connectors. The far end must be terminated with 50 ohms in order to avoid reflections. Typically, a voltage-divider network is used, in order to restore the appropriate DC bias, as per the LVPECL standard.
The LVDS outputs are not buffered, do not have any termination and are DC coupled. Care must be taken to avoid applying an external DC potential to this terminal. If configured for CMOS mode, the output shunt must be replaced with a series-termination resistor of 10 ohms, to prevent ringing and to protect the AD9517 in the event of an output short circuit.
The CMOS outputs use an SN65LVDS32 differential receiver chip to convert the LVDS output from the AD9517 to 3.3V CMOS levels. Note that the output may be loaded with 50 ohms, with reduced swing (500 mVpp).
Communications
The clock generator interfaces to an external host for register programming and health monitoring functions through a Modbus/RTU interface. A MAX3072 RS-485 transceiver is used to interface the bidirectional differential RS-485 bus with the MCU USART.
A baud rate of 57600 is used, with 8 data bits, Even parity and 1 stop bit (8E1).
In the event that multiple clock generator units are needed in a system, they may be phase-synchronized through a SYNC input. The SYNC input uses the LVDS signalling scheme. Driving SYNC causes the internal counters used in the dividers to reset.
The Modbus/RTU and SYNC signals are brought to a 9-pin male CPC connector.
Power Supply
The power supply network used on the clock generator board is designed to reduce the effect of ripple and noise on the incoming supply. The input voltage can range from 10V to 15V DC, 500 mA. Operation beyond 15V is possible, however the heat dissipation may be excessive.
A linear preregulator, based on the LM317 is used to reduce the input voltage down to an 8V preregulator voltage. The LM317 uses heavy filtering on the reference pin, to improve the ripple rejection specifications of the LM317.
A discrete shunt regulator, based on an op-amp, is used to generate a clean voltage from the LM317 output. The design is described on the Wenzel Associates website.
The cleaned-up voltage is then regulated down to 5V (charge pump) and 3.3V (PLL) supplies. The charge pump supply uses the ADP3334 500 mA LDO, the PLL supply uses the TPS77833 750 mA LDO. A separate 3.3V supply for the MCU is derived from the preregulator output (using an ADP3334) in order to avoid contaminating the clean voltage with digital switching noise.
Indicators
The overall health and operating condition is presented visually using a single bi-color LED indicator. The LED glows red to indicate a fault or error condition, such as overvoltage, overtemperature or loss of reference. If the LED is green, then all monitored parameters are within tolerance. The LED flashes briefly to indicate that the clock synthesizer is being addressed through the Modbus/RTU interface.
Two board-mounted LEDs are also present, to indicate power-OK and PLL lock. These are not normally visible when the clock generator is mounted within the RF-tight enclosure.
Modbus Registers
The interface to the synthesizer is through Modbus/RTU. The Modbus communications model is a single master controlling various slave devices[1]. Each slave is addressable, and has different registers which may be read or written. This design implements read-only registers (referred to as Input Registers in the Modbus specifications) and read-write registers (Holding Registers). There are no coils or status bits available.
Input Registers
The available input registers are shown in the table below.
| Register Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | ID | Returns the device identification (currently 0x0101) |
| 1001 | REVISION | Returns the device revision. The lower byte is the sub-revision, the upper byte is the integer part of the revision number. For example, a revision code of 0x0100 represents version 1.0 |
| 1002 | ALARM | Indicates the cause of any alarms indicated by the Modbus ALM signal. Reading the register clears the alarm condition and deasserts the Modbus ALM signal. |
| 1003 | TEMP | Read back the temperature sensor on board. The value returned is in hundredths of a degree centigrade. For example, a readback code of 4538 represents 45.38 degrees centigrade. |
| 1004 | VOLT_CPU | Returns the current CPU supply voltage, in thousandths of a volt. The nominal voltage is 5V. |
| 1005 | VOLT_PLL | Returns the current PLL supply voltage, in thousandths of a volt. The nominal voltage is 3.3V. |
| 1006 | VOLT_CP | Returns the current charge pump supply voltage, in thousandths of a volt. The nominal voltage is 5V. |
| 1007 | VOLT_PR | Returns the current pre-regulator voltage, in thousandths of a volt. The nominal voltage is 8V. This voltage also powers the VCO. |
Input Register Map
| 7-5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reserved | Voltage out of range | Temperature out of range | VCO stopped | Reference stopped | Lock detect failure |
ALARM register (1002)
Holding Registers
The holding registers are divided into two parts. The first set of registers map directly to those on the AD9517 clock generator chip. The second set affect operation of the synthesizer unit as a whole. In both cases, writing to these registers is a non-volatile operation, and the settings are stored in an on-board EEPROM.
AD9517 Registers
| Addr (Hex) | Name | Bit 7 | Bit 6 | Bit 5 | Bit 4 | Bit 3 | Bit 2 | Bit 1 | Bit 0 | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00 | Port Configuration | SDO active | LSB first | Soft Reset | Long Instruction | Long Instruction | Soft Reset | LSB first | SDO active | Not saved to EEPROM |
| 04 | Read Back Control | Blank | Read Back Active Registers | Not saved to EEPROM | ||||||
| 10 | CPCFG | PFD Polarity | Charge Pump Current | Charge Pump Mode | Power Down Mode | |||||
| 11 | R Counter | R divider bits 7:0 | ||||||||
| 12 | Blank | R divider bits 13:8 | ||||||||
| 13 | A Counter | Blank | A counter | |||||||
| 14 | B Counter | B divider bits 7:0 | ||||||||
| 15 | Blank | B divider bits 12:8 | ||||||||
| 16 | PLLCTL1 | Set CP to | Reset R counter | Reset A and B counters | Reset all counters | B counter bypass | Prescaler | |||
| 17 | PLLCTL2 | STATUS pin control | Anti-backlash pulse width | For correct operation, STATUS pin should indicate DLD, reference and VCO status | ||||||
| 18 | PLLCTL3 | Reserved | Lock Detect Counter | Digital Lock Detect Window | Disable Digital Lock Detect | VCO Cal Divider | VCO Cal Now | |||
| 19 | PLLCTL4 | R,A,B counters SYNC pin reset | R path delay | N path delay | ||||||
| 1A | PLLCTL5 | Reserved | Ref Freq monitor threshold | LD pin control | For correct operation, LD should be set to analog lock detect | |||||
| 1B | PLLCTL6 | VCO Freq monitor | REF2 Freq monitor | REF1 Freq monitor | REFMON pin control | |||||
| 1C | PLLCTL7 | Disable switch deglitch | Select REF2 | Use REFSEL | Auto switch | Stay on REF2 | REF2 power on | REF1 power on | Diff. ref. | This design requires the use of Diff. ref. |
| 1D | PLLCTL8 | Reserved | PLL Status Disable | LD comparator disable | Holdover enable | Ext. holdover control | Holdover enable | Enable LD comparator for proper operation | ||
| 1F | PLL Readback | Reserved | VCO Cal Done | Holdover active | REF2 Selected | VCO freq. > threshold | REF2 freq. > threshold | REF1 freq. > threshold | Digital Lock Detect | |
| A0 | OUT4 delay bypass | Blank | OUT4 delay bypass | |||||||
| A1 | OUT4 delay full-scale | Blank | Ramp Capacitors | Ramp Current | ||||||
| A2 | OUT4 delay fraction | Blank | OUT4 delay fraction | |||||||
| A3 | OUT5 delay bypass | Blank | Delay bypass | |||||||
| A4 | OUT5 delay full-scale | Blank | Ramp Capacitors | Ramp Current | ||||||
| A5 | OUT5 delay fraction | Blank | Delay fraction | |||||||
| A6 | OUT6 delay bypass | Blank | Delay bypass | |||||||
| A7 | OUT6 delay full-scale | Blank | Ramp Capacitors | Ramp Current | ||||||
| A8 | OUT6 delay fraction | Blank | Delay fraction | |||||||
| A9 | OUT7 delay bypass | Blank | Delay bypass | |||||||
| AA | OUT7 delay full-scale | Blank | Ramp Capacitors | Ramp Current | ||||||
| AB | OUT7 delay fraction | Blank | Delay fraction | |||||||
| F0 | OUT0 | Blank | Invert | Diff. Voltage | Power Down | |||||
| F1 | OUT1 | Blank | Invert | Diff. Voltage | Power Down | |||||
| F4 | OUT2 | Blank | Invert | Diff. Voltage | Power Down | |||||
| F5 | OUT3 | Blank | Invert | Diff. Voltage | Power Down | |||||
| 140 | OUT4 | CMOS Polarity | Invert | CMOS B | LVDS/CMOS | LVDS current | Power Down | |||
| 141 | OUT5 | CMOS Polarity | Invert | CMOS B | LVDS/CMOS | LVDS current | Power Down | Output must be set to LVDS mode | ||
| 142 | OUT6 | CMOS Polarity | Invert | CMOS B | LVDS/CMOS | LVDS current | Power Down | Output must be set to LVDS mode | ||
| 143 | OUT7 | CMOS Polarity | Invert | CMOS B | LVDS/CMOS | LVDS current | Power Down | |||
| 190 | Divider 0 (PECL) | Low Cycles | High Cycles | |||||||
| 191 | Bypass | Nosync | Force High | Start High | Phase Offset | |||||
| 192 | Blank | Reserved | Direct to Output | DCCOFF | ||||||
| 196 | Divider 1 (PECL) | Low Cycles | High Cycles | |||||||
| 197 | Bypass | Nosync | Force High | Start High | Phase Offset | |||||
| 198 | Blank | Reserved | Direct to Output | DCCOFF | ||||||
| 199 | Divider 2 (LVDS, CMOS) | Low Cycles (2.1) | High Cycles (2.1) | |||||||
| 19A | Phase offset (2.2) | Phase offset (2.1) | ||||||||
| 19B | Low Cycles (2.2) | High Cycles (2.2) | ||||||||
| 19C | Reserved | Bypass 2.2 | Bypass 2.1 | Nosync | Force High | Start High 2.2 | Start High 2.1 | |||
| 19D | Blank | Reserved | DCCOFF | |||||||
| 19E | Divider 3 (LVDS, CMOS) | Low Cycles (3.1) | High Cycles (3.1) | |||||||
| 19F | Phase offset (3.2) | Phase offset (3.1) | ||||||||
| 1A0 | Low Cycles (3.2) | High Cycles (3.2) | ||||||||
| 1A1 | Reserved | Bypass 3.2 | Bypass 3.1 | Nosync | Force High | Start High 3.2 | Start High 3.1 | |||
| 1A2 | Blank | Reserved | DCCOFF | |||||||
| 1E0 | VCO Divider | Blank | Reserved | VCO Divider | ||||||
| 1E1 | Input CLKs | Reserved | Power down Clock Input | Power down VCO Clock | Power down Select VCO/Clk | Bypass VCO divider | ||||
| 230 | Power Down and Sync | Reserved | Power down Sync | Power down dist. ref. | Soft Sync | |||||
| 232 | Update All | Reserved | Update all regs | Required after changing any registers | ||||||
Input Registers - AD9517
Additional information about the function of each register may be obtained from the AD9517 data sheet[2].
Other Holding Registers
| Register Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 | TEMP_MIN | Minimum temperature, if the current temperature falls below this value, an alarm is generated. |
| 1001 | TEMP_MAX | Maximum temperature, if the current temperature goes above this value, an alarm is generated. |
| 1002 | VOLT_CPU_MIN | Minimum CPU voltage before an alarm is flagged. |
| 1003 | VOLT_CPU_MAX | Maximum CPU voltage before an alarm is flagged. |
| 1004 | VOLT_PLL_MIN | Minimum PLL voltage before an alarm is flagged. |
| 1005 | VOLT_PLL_MAX | Maximum PLL voltage before an alarm is flagged. |
| 1006 | VOLT_CP_MIN | Minimum Charge pump voltage before an alarm is flagged. |
| 1007 | VOLT_CP_MAX | Maximum Charge pump voltage before an alarm is flagged. |
| 1008 | VOLT_PR_MIN | Minimum pre-regulator voltage before an alarm is flagged. |
| 1009 | VOLT_PR_MAX | Maximum pre-regulator voltage before an alarm is flagged. |
Input Register Map
Connectors
| Refdes | Purpose | Type |
|---|---|---|
| J1 | In-system Programming Port | 6-pin Pin header |
| J2 | LED port | 8-pin Solderable connections |
| J3 | GPIO port | 12-pin Solderable connections |
| J4, J6 | OUT0 LVPECL P/N Outputs | SMA female |
| J5, J7 | OUT2 LVPECL P/N Outputs | SMA female |
| J8,J9 | OUT4 LVPECL/CMOS P/N Outputs | SMA female |
| J10 | Reference Clock Input | SMB female |
| J11,J12 | OUT6 LVPECL/CMOS P/N Outputs | SMA female |
| J13 | OUT7 CMOS Output | SMA female |
| J14 | Modbus/RTU Interface | 10-pin shrouded header |
| J15 | Modbus/RTU Interface sub-assembly external connector | 9-pin CPC series 2 chassis-mount |
| J16 | OUT5 CMOS Output | SMA female |
| J17 | Power input connector | 2-pin Solderable connections |
| J18 | VCO supply voltage selection jumper | Pin header |
| J19 | Modbus/RTU Interface sub-assembly internal connector | 10-pin shrouded header |
| J20 | Spare OUT3 LVPECL P/N Outputs | 4-pin Solderable connections |
| J21 | Spare OUT1 LVPECL P/N Outputs | 4-pin Solderable connections |
| J22 | Extra I/Os from Modbus/RTU Interface sub-assembly | 4-pin Solderable connections |
List of Connectors
In-System Programming Port
This connector permits the ATmega164P Flash and EEPROM to be programmed during development. It is designed to mate with the Atmel AVRISP mkII programming cable.
| Pin | Signal |
|---|---|
| 1 | MISO |
| 2 | +5V |
| 3 | SCK |
| 4 | MOSI |
| 5 | RESET |
| 6 | GND |
J1 (In-System Programming Port)
LED Port
This connector allows connections to various LEDs
| Pin | Signal | Pin | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Power LED | 2 | GND |
| 3 | LED 1 | 4 | GND |
| 5 | LED 2 | 6 | GND |
| 7 | Locked LED | 8 | GND |
J2 (LED Port)
When an external bi-color LED is used, the LED is connected between pins 3 and 5.
GPIO port
This connector provides access to general purpose I/O from the MCU
| Pin | Signal | Pin | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | 2 | GPIO3 |
| 3 | GND | 4 | GPIO2 |
| 5 | GND | 6 | GPIO1 |
| 7 | GND | 8 | GPIO0 |
| 9 | GND | 10 | AIN1 |
| 11 | GND | 12 | AIN2 |
J3 (GPIO)
Pins 10 and 12 (AIN1, AIN2) can also be used as analog inputs.
Modbus/RTU Interface
The Modbus/RTU interface sub-assembly connects to this port.
| Pin | Signal | Pin | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | 2 | EXTIO1 |
| 3 | B | 4 | EXTIO2 |
| 5 | GND | 6 | GND |
| 7 | SYNC_N | 8 | EXTIO3 |
| 9 | SYNC_P | 10 | EXTIO4 |
J14 (Modbus/RTU interface)
Modbus/RTU Interface subassembly external connector
This connector on the Modbus/RTU interface sub-assembly is the external connection to Modbus/RTU.
| Pin | Signal |
|---|---|
| 1 | A |
| 2 | EXTIO1 |
| 3 | B |
| 4 | EXTIO2 |
| 5 | GND |
| 6 | EXTIO3 |
| 7 | SYNC_N |
| 8 | EXTIO4 |
| 9 | SYNC_P |
J15 (Modbus/RTU Interface subassembly external connector)
Input Power
This connector provides power to the board. This connector provides reverse-voltage protection.
| Pin | Signal |
|---|---|
| 1 | +15V |
| 2 | GND |
J17 (Input Power)
VCO voltage selection
This header permits the VCO voltage to be selected.
| Pin | Signal |
|---|---|
| 1 | VCLEAN |
| 2 | V_VCO |
| 3 | VCP |
J18 (VCO voltage selection)
To select 8V VCO operation, bridge pins 1 and 2, else bridge pins 2 and 3 for 5V VCO
Modbus/RTU Interface subassembly internal connector
This connector on the Modbus/RTU interface sub-assembly connects to the main board.
| Pin | Signal | Pin | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | 2 | EXTIO1 |
| 3 | B | 4 | EXTIO2 |
| 5 | GND | 6 | GND |
| 7 | SYNC_N | 8 | EXTIO3 |
| 9 | SYNC_P | 10 | EXTIO4 |
J19 (Modbus/RTU Interface subassembly internal connector)
Spare OUT3 LVPECL outputs
This connector brings out OUT3 outputs.
| Pin | Signal | Pin | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | OUT_N | 2 | GND |
| 3 | OUT_P | 4 | GND |
J20 (Spare OUT3 LVPECL outputs)
Spare OUT1 LVPECL outputs
This connector brings out OUT1 outputs.
| Pin | Signal | Pin | Signal |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | OUT_N | 2 | GND |
| 3 | OUT_P | 4 | GND |
J21 (Spare OUT1 LVPECL outputs)
Extra I/O from Modbus/RTU interface subassembly
This connector brings out OUT1 outputs.
| Pin | Signal |
|---|---|
| 1 | EXTIO1 |
| 2 | EXTIO2 |
| 3 | EXTIO3 |
| 4 | EXTIO4 |
J22 (Extra I/O from Modbus/RTU interface subassembly)
These I/Os are not assigned to any specific task on the board, and may be used for future expansion, or connected to, for example, the J20 and J21 to allow access to two additional LVPECL outputs.
Other Resources
References
- ↑ http://www.modbus.org/specs.php Modbus specifications
- ↑ http://www.analog.com/static/imported-files/data_sheets/AD9517_3.pdf AD9517 Data sheet
External Links
- http://www.analog.com Analog Devices website
- http://www.atmel.com Atmel website
- http://www.wenzel.com Wenzel Associates website. Useful information about clock sources.
- http://www.maxim-ic.com Maxim Semiconductor website
- http://www.minicircuits.com Mini-circuits website
- http://www.ti.com Texas Instruments website